Blog
What is a Horizontal Machining Center and How Does It Work
A horizontal machining center is a pivotal machine tool in modern manufacturing, renowned for its precision and efficiency in machining complex parts. As the name suggests, this type of equipment features a horizontal spindle orientation, which allows for the use of various cutting tools and facilitates operations such as drilling, milling, and tapping. This unique design significantly enhances accessibility to the workpiece from multiple angles, effectively reducing setup time and improving the overall production cycle.
Understanding how a horizontal machining center operates is crucial for professionals in the manufacturing sector. The center’s programmable controls and advanced automation capabilities empower operators to execute intricate machining tasks with remarkable speed and accuracy. This capability not only optimizes the workflow but also supports the production of high-tolerance components critical in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. By delving into the mechanics and operational principles of horizontal machining centers, we can better appreciate their role in advancing industrial technology and meeting the evolving demands of modern engineering.

Definition and Overview of Horizontal Machining Centers
Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) are advanced pieces of machinery utilized primarily in the manufacturing sector for precision machining processes. These equipment are characterized by their horizontal spindle orientation, which allows for greater stability and enhanced cutting performance, especially for larger or heavier workpieces. HMCs are designed to perform various operations, including milling, drilling, and tapping, often in a single setup, which significantly increases efficiency and reduces cycle times.
The architecture of a horizontal machining center typically includes a rotating spindle mounted horizontally on a robust bed, with multiple axes of motion that facilitate intricate and complex machining tasks. The design often incorporates a tool changer and a workpiece pallet system, permitting the seamless transition between different operations without the need for manual intervention. This automation not only streamlines production processes but also minimizes the potential for error, thereby ensuring high-quality output. Overall, the functionality and versatility of horizontal machining centers make them a critical component in modern manufacturing environments.
Key Components and Features of Horizontal Machining Centers
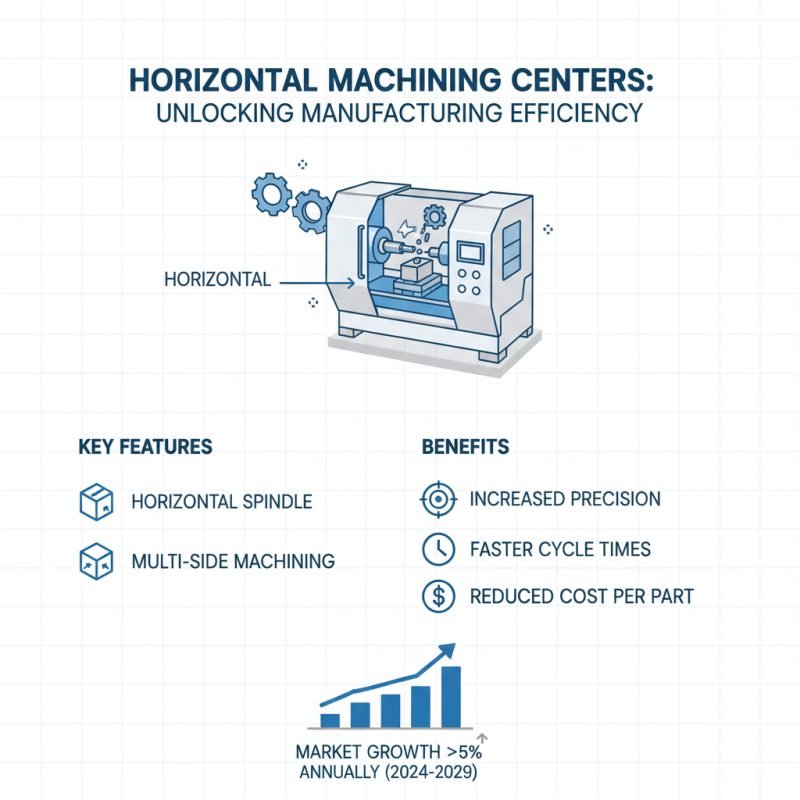
Horizontal machining centers (HMCs) are vital machines in the manufacturing industry, particularly for their efficiency in handling complex parts with high precision. Key components of HMCs include a horizontal spindle, which allows for better chip removal and facilitates cutting operations on multiple sides of a workpiece simultaneously. This design not only improves machining accuracy but also enhances productivity by reducing the overall cycle time. Industry reports indicate that HMCs are gaining popularity due to their ability to produce parts at a lower cost, leading to a projected market growth of over 5% annually through the next five years.
Additionally, a significant feature of horizontal machining centers is their ability to integrate with automation systems. This allows for increased flexibility and reduces human error, resulting in higher operational efficiency. Most modern HMCs are equipped with advanced control systems, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustments, which contribute to maintaining optimal performance. Data shows that manufacturers utilizing advanced HMCs report a decrease in operational costs by up to 30%, demonstrating their effectiveness in lean manufacturing environments.
Tips: When selecting a horizontal machining center, consider the workpiece size and complexity, as well as the specific machining processes required. Ensuring your HMC is equipped with the right tools and fixtures can enhance its performance and versatility. Additionally, regular maintenance and updates to the control system will extend the life of your machining center and ensure consistent output quality.
Principles of Operation: How Horizontal Machining Centers Work

Horizontal machining centers (HMCs) are essential tools in modern manufacturing, primarily utilized for precision machining of complex parts. The workings of these machines are based on a unique design that allows for the horizontal positioning of the spindle. This orientation facilitates efficient chip removal and enhances cutting stability, resulting in improved surface finish and dimensional accuracy. According to a report by ARC Advisory Group, HMCs can achieve productivity gains of up to 30% compared to vertical machining centers, making them a preferred choice in high-demand manufacturing applications.
The principles of operation of an HMC involve an integrated process of automated tool changes and multi-axis movement. These machines are typically equipped with a rotary table that permits the workpiece to be positioned at various angles during machining, which minimizes repositioning and setup time. This multi-axis capability allows simultaneous cutting in multiple directions, greatly increasing the efficiency of complex operations. The latest industry data indicates that HMCs equipped with advanced controls and AI capabilities can further enhance machining efficiency, reducing cycle times by up to 40%.
Tips for maximizing the performance of a horizontal machining center include regular maintenance of the cutting tools and machine components to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, utilizing high-efficiency milling strategies can significantly improve material removal rates. Manufacturers should also consider implementing automation solutions that can help streamline workflows, leading to enhanced operational productivity.
Applications and Industries Utilizing Horizontal Machining Centers
Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) are widely utilized across various industries for their exceptional efficiency and precision in machining tasks. In automotive manufacturing, HMCs play a crucial role in creating complex engine components, transmission housings, and other critical parts. Their ability to handle multiple operations in a single setup reduces cycle times and increases productivity, making them essential for high-volume production environments. This versatility allows manufacturers to create intricate geometries with consistent quality, which is vital in maintaining a competitive advantage in the automotive sector.
Another significant application of HMCs is in the aerospace industry, where precision and reliability are paramount. HMCs are utilized to fabricate components such as turbine housings, brackets, and structural elements that require tight tolerances. The robust design and advanced tooling capabilities of HMCs enable them to work with a variety of materials, from aluminum alloys to high-strength steel, further enhancing their utility in this field. Additionally, the programming flexibility of HMCs allows for rapid adaptation to changes in design specifications, ensuring that manufacturers can meet dynamic market demands while maintaining stringent quality standards.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Horizontal Machining Centers
Horizontal machining centers (HMCs) offer a unique blend of advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for specific production needs. One of the primary advantages of HMCs is their ability to handle large workpieces and complex geometries with precision. The horizontal setup allows for better chip removal and coolant flow, which minimizes overheating and maintains high tolerances during machining. This configuration also facilitates easier setups and quicker tool changes, enhancing productivity in a multi-tasking environment.
However, the disadvantages of horizontal machining centers should not be overlooked. They typically come with a higher initial investment and maintenance costs compared to vertical machining centers. Additionally, HMCs may require more floor space, which could be a limiting factor for smaller workshops. Moreover, programming and operating these machines can be more complex, necessitating skilled operators who are familiar with horizontal machining processes.
**Tips:** When considering an HMC for your operation, assess your production volumes and types of parts you intend to machine. If your work involves larger components or requires consistent precision, an HMC may be a worthwhile investment. However, ensure that your team possesses the necessary expertise to operate the machine efficiently.
What is a Horizontal Machining Center and How Does It Work - Advantages and Disadvantages of Horizontal Machining Centers
| Feature | Horizontal Machining Centers |
|---|---|
| Axis Configuration | Typically 3 to 5 axes |
| Workpiece Orientation | Horizontal |
| Tool Change Speed | Fast tool change capabilities |
| Setup Time | Reduced setup time due to automatic tool changers |
| Machining Precision | High precision and repeatability |
| Advantages | Efficient for mass production, better chip removal, reduced floor space needed |
| Disadvantages | Higher initial cost, complexity in operation and maintenance |
| Applications | Aerospace, automotive, precision engineering |
Related Posts
-

Unlock Precision: How a Small CNC Mill Transforms Your DIY Projects into Professional Creations
-

How to Identify Top Suppliers for the Best CNC Equipment: A Comprehensive Guide
-

Exploring the Advancements in Milling Machine Technology for Modern Manufacturing
-

7 Must Have Features of the Best Machining Center for Your Business
-

How to Choose the Best Small CNC Machine in 2025 with Emerging Technology Trends
-

How to Choose the Right Small CNC Machine for Your Workshop Needs